Advertiser Disclosure
Last update: June 11, 2025
7 minutes read
How Does FAFSA Verify Assets and Does It Affect Eligibility for Aid?
How does FAFSA verify assets, and what documents are required? Learn the step-by-step FAFSA verification process, common mistakes to avoid, and expert tips to prepare.

By Derick Rodriguez, Associate Editor
Edited by Brian Flaherty, B.A. Economics
Learn more about our editorial standards



By Derick Rodriguez, Associate Editor
Edited by Brian Flaherty, B.A. Economics
Learn more about our editorial standards
Navigating the FAFSA verification process doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. With a clear understanding of which assets to report and how the government now measures your family’s financial contribution, you can complete your application accurately and maximize your aid.
In this guide, we’ll answer "What is fafsa verification?", explain how does fafsa verify assets, and simplify the fafsa verification process—so you can file with confidence and avoid common pitfalls.

Key takeaways
- FAFSA verification affects about one-third of all applicants and can affect your financial aid eligibility
- Using the IRS Data Retrieval Tool can significantly reduce the chances of being selected for verification
- Remember that verification is a normal part of the process and doesn't mean you've done anything wrong
What is FAFSA verification, and why does it matter?
FAFSA verification is a process used by the Department of Education and schools to ensure the accuracy of information provided on the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). It's not an audit or indication of wrongdoing, but rather a routine check to maintain the integrity of the financial aid system.
Remember, one of the best ways to manage a potential FAFSA verification is to provide honest and accurate information in the first place. That way, if verification occurs, you can stand by your answers and confirm their accuracy - or work to correct any honest mistakes that occurred in the process.
Why it matters:
- Verification can affect your eligibility for need-based aid
- Inaccuracies discovered during verification may lead to changes in your aid package
- Understanding the process helps you prepare and respond effectively
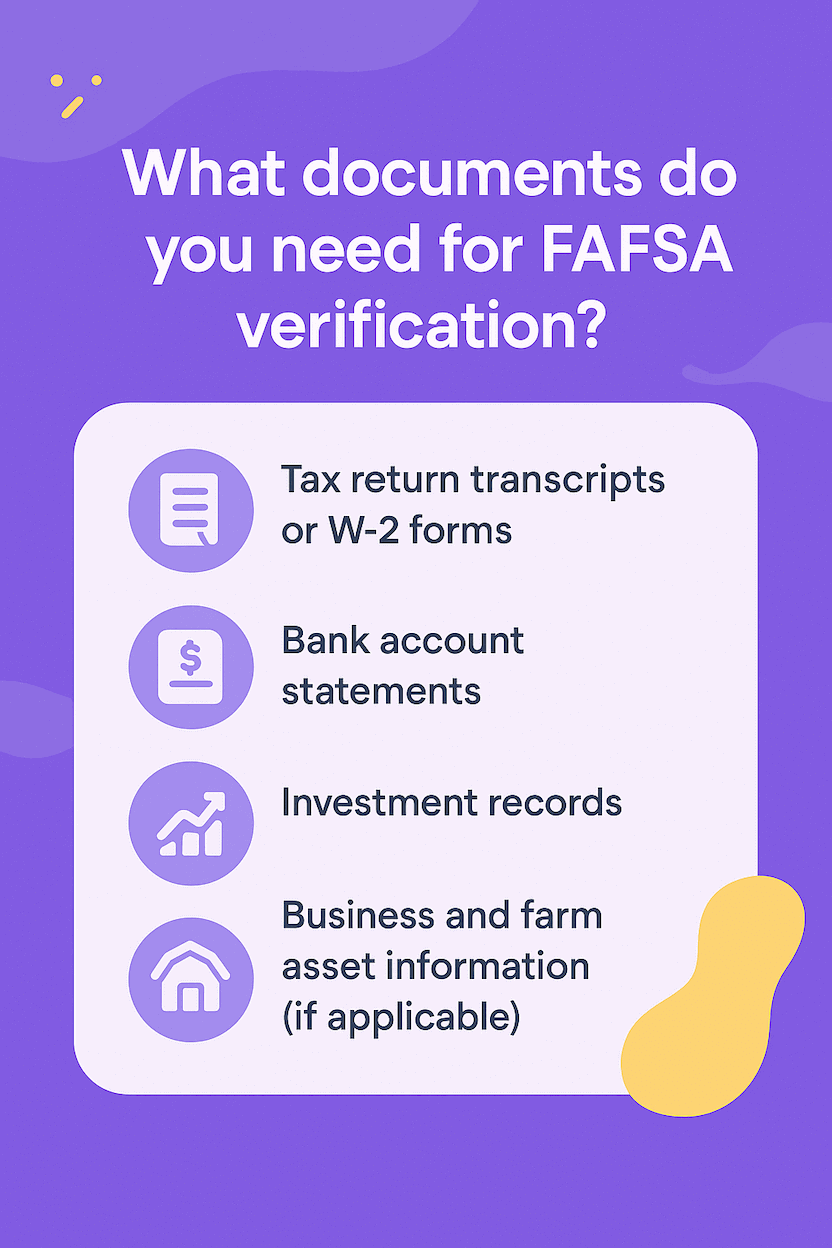
What documents do you need?
To streamline the verification process, gather these key documents:
- Tax return transcripts or W-2 forms
- Bank account statements
- Investment records
- Business and farm asset information (if applicable)

TuitionHero Tip
Create a "FAFSA Folder" (physical or digital) to keep all these documents organized and easily accessible.
Using the IRS Data Retrieval Tool: This tool automatically transfers your tax information to your FAFSA, reducing errors and the likelihood of being selected for verification.
Counted vs. excluded assets
When filling out your FAFSA, it’s crucial to know exactly which assets you must report and which you can safely not report. Clear reporting helps prevent verification delays and ensures you only submit what’s required.
Many applicants wonder "Does FAFSA look at assets beyond income?", but the Department of Education only asks you to verify assets in specific categories.
Assets you MUST report:
- Cash, checking, and savings accounts: Total balances as of the FAFSA “snapshot” date
- Net worth of additional property: Vacation homes, rental real estate, or land (current market value minus debt)
- Investment accounts: Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, non-529 education savings you own
- Business/farm value: Net worth of any family-owned enterprise, excluding debt on the operation
- UGMA/UTMA accounts: Custodial accounts owned by the student
Assets you DON’T report:
- Primary residence equity: The home you live in is excluded
- Retirement accounts: 401(k)s, IRAs, pensions, annuities
- Life insurance policies and ABLE accounts
- 529 plans owned by grandparents: Report only when distributions are made to you
- Vehicles and personal belongings

TuitionHero Tip
If your parents’ income is under $60,000 or your household receives means-tested benefits (SNAP, Medicaid, etc.), you may skip asset reporting altogether—check the FAFSA instructions to confirm eligibility.
A step-by-step guide to verify assets
- Receiving the verification notice: You'll be notified through your school or a note on your FAFSA Submission Summary.
- Completing the verification worksheet: Your school will provide this form to collect additional information.
- Submitting documentation: Provide all requested documents promptly to your school's financial aid office.
- Timeline: The process typically takes 2-4 weeks once all documents are submitted.

How to overcome common challenges
- Discrepancies in reported information: Double-check all entries and be prepared to explain any inconsistencies.
- Missing documents: Contact the relevant institutions (e.g., banks, employers) to obtain any missing paperwork quickly.
- Deadline pressure: Start the process early and communicate with your financial aid office if you anticipate delays.
What could verification mean for your financial aid?
Verification can lead to changes in your Student Aid Index (SAI) and, consequently, your aid package. However, significant changes are relatively rare.
In fact, in many cases, verification doesn’t result in any changes at all. Remember, just because the Department of Education wants to double-check some information doesn’t mean that the information is wrong. Some applications are even picked randomly, not because of any particular red flag!

TuitionHero Tip
Some states offer free college tuition for certain income brackets, regardless of verification outcomes!
Expert strategies for the verification process
- Respond promptly: Every day counts in securing your aid package.
- Double-check everything: A second look can catch errors before submission.
- Communication is key: Work closely with your financial aid office for guidance.
Compare private student loans now
TuitionHero simplifies your student loan decision, with multiple top loans side-by-side.
Compare Rates
The shift from EFC to Student Aid Index (SAI)
As of the 2024–25 award year, the old Expected Family Contribution (EFC) has been replaced by the Student Aid Index (SAI)—a more transparent way to gauge your federal aid eligibility.
Though the goal remains the same (measuring how much you and your family can contribute), SAI introduces new features that can benefit low-income students.
Understanding what is the process of verification for FAFSA helps you see how your SAI feeds into aid decisions and gives you tools to verify FAFSA entries before submission.
- Negative SAI values: Families with very limited resources can qualify for additional grants
- Greater clarity: SAI’s formula and the online estimator on StudentAid.gov let you preview your index before filing
- Consistent terminology: Your “aid index” now aligns across federal and institutional need-analysis systems
A lower (or negative) SAI directly translates into more need-based aid, so understanding this shift can help you plan your application strategy—and maximize grant opportunities—well before deadlines.
Beyond verification: Next steps in your financial aid journey
- Review your updated aid offer carefully
- Understand the appeals process for special circumstances
- Start planning early for future FAFSA applications

Why trust TuitionHero
At TuitionHero, we help make paying for college easier. We offer guidance on student loans, scholarships, and refinancing. Plus, we provide insights on using credit cards to manage education costs and save on interest.
Surge in FAFSA submissions
As of March 17, 2025, the U.S. Department of Education reported that over 8 million 2025–26 FAFSA® forms had been successfully submitted and processed—nearly a 50% increase compared to the same point last year
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
The FAFSA verification process usually takes about 2-4 weeks once all required documents are submitted to your school's financial aid office.
However, this timeline can vary depending on the complexity of your financial situation and the workload of your school's financial aid department. It's crucial to submit all requested documents promptly to avoid delays in receiving your financial aid package.
Yes. Being selected for verification doesn't disqualify you from receiving financial aid. It's simply an extra step to ensure the accuracy of the information on your FAFSA.
As long as you provide the requested documentation and the information matches what you reported on your FAFSA, you'll still be eligible for financial aid. In some cases, verification might even result in an increase in your aid package if it reveals that you're eligible for more assistance.
If you're unable to provide some of the requested verification documents, don't panic. Contact your school's financial aid office immediately to explain your situation. They may be able to suggest alternative documents or ways to verify your information.
In some cases, they might be able to use professional judgment to make adjustments based on your unique circumstances. The key is to communicate openly and honestly with your financial aid administrators.
While there's no guaranteed way to avoid verification, you can reduce your chances by using the IRS Data Retrieval Tool when filing your FAFSA. This tool automatically transfers your tax information directly from the IRS to your FAFSA, reducing the likelihood of errors.
Additionally, double-check all information before submitting your FAFSA, avoid leaving fields blank, and be consistent with the information you provide.
The single most frequent error on FAFSA applications is leaving required fields blank or entering “zero” incorrectly. Applicants often skip a question—usually about income, assets, or household size—and fail to go back to fill it in.
Even a single blank can prevent your application from processing or trigger verification, delaying your aid.
To avoid this, double-check every section, use the FAFSA’s built-in error checker before submitting, and make sure you sign and submit the form electronically.
Assets aren’t automatically checked for every applicant. About one-third of filers are randomly selected for FAFSA verification.
At this point, you’ll be asked to submit FAFSA verification documents—typically tax transcripts, bank statements, and investment or business records.
Your school’s financial aid office then compares those documents to your application entries to verify assets and resolve any discrepancies before finalizing your aid.
Final thoughts
By mastering exactly which assets to report and embracing the updated Student Aid Index system, you’ll streamline your FAFSA experience and strengthen your eligibility for need-based aid.
Remember to gather your FAFSA verification documents early, use the IRS Data Retrieval Tool whenever possible, and review your SAI estimate before submission.
If you’re ever selected for a FAFSA audit, having organized records will help you respond quickly. With these insights and a clear grasp of what is FAFSA verification, you can confidently complete your application and focus on your educational journey.
Source
- Guide To FAFSA Verification | Bankrate
- Documents Needed for the FAFSA and Other Financial Aid Forms | Appily
- Yes, FAFSA Verifies Assets and Here’s How | Grantford Financial Aid Blog
- Guide To FAFSA Verification | Bankrate
- Verifying Assets | Knowledge Center
- 2025-26 FAFSA Checklist: What You’ll need to Complete Your Application | Fastweb
- Verification - Finaid
- Reporting Your Assets on the FAFSA | Discover Student Loans
- 6 Things Students Need Before They Fill Out the 2024–25 FAFSA® Form
- Filling Out the FAFSA | 2024-2025 Federal Student Aid Handbook
Author

Derick Rodriguez
Derick Rodriguez is a seasoned editor and digital marketing strategist specializing in demystifying college finance. With over half a decade of experience in the digital realm, Derick has honed a unique skill set that bridges the gap between complex financial concepts and accessible, user-friendly communication. His approach is deeply rooted in leveraging personal experiences and insights to illuminate the nuances of college finance, making it more approachable for students and families.
Editor

Brian Flaherty
Brian is a graduate of the University of Virginia where he earned a B.A. in Economics. After graduation, Brian spent four years working at a wealth management firm advising high-net-worth investors and institutions. During his time there, he passed the rigorous Series 65 exam and rose to a high-level strategy position.
At TuitionHero, we're not just passionate about our work - we take immense pride in it. Our dedicated team of writers diligently follows strict editorial standards, ensuring that every piece of content we publish is accurate, current, and highly valuable. We don't just strive for quality; we aim for excellence.
Related posts
While you're at it, here are some other college finance-related blog posts you might be interested in.
Shop and compare student financing options - 100% free!

Always free, always fast
TuitionHero is 100% free to use. Here, you can instantly view and compare multiple top lenders side-by-side.

Won’t affect credit score
Don’t worry – checking your rates with TuitionHero never impacts your credit score!

Safe and secure
We take your information's security seriously. We apply industry best practices to ensure your data is safe.
Finished scrolling? Start saving & find your private student loan rate today
Compare Personalized Rates


